|
24.5.2016 |
EN |
Official Journal of the European Union |
L 135/11 |
REGULATION (EU) 2016/792 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
of 11 May 2016
on harmonised indices of consumer prices and the house price index, and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95
(Text with EEA relevance)
THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND THE COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION,
Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, and in particular Article 338(1) thereof,
Having regard to the proposal from the European Commission,
After transmission of the draft legislative act to the national parliaments,
Having regard to the opinion of the European Central Bank (1),
Acting in accordance with the ordinary legislative procedure (2),
Whereas:
|
(1) |
The harmonised index of consumer prices (HICP) is designed to measure inflation in a harmonised manner across Member States. The Commission and the European Central Bank (ECB) use the HICP in their assessment of price stability in the Member States under Article 140 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (TFEU). |
|
(2) |
Harmonised indices are used in the context of the Commission’s macroeconomic imbalance procedure, as established by Regulation (EU) No 1176/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council (3). |
|
(3) |
Price statistics of high quality and comparability are essential for those responsible for public policy in the Union, researchers and all European citizens. |
|
(4) |
The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) uses the HICP as an index in order to measure the achievement of the ESCB’s price stability objective under Article 127(1) TFEU, which is of particular relevance for the definition and implementation of the monetary policy of the Union under Article 127(2) TFEU. Pursuant to Articles 127(4) and 282(5) TFEU, the ECB is to be consulted on any proposed Union act in its fields of competence. |
|
(5) |
The objective of this Regulation is to establish a common framework for the development, production and dissemination of harmonised indices of consumer prices and of the house price index (HPI) at Union and national level. This does not preclude, however, the possibility of extending the application of the framework, in the future, if necessary, to the subnational level. |
|
(6) |
Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 (4) established a common framework for setting up harmonised indices of consumer prices. That legal framework needs to be adapted to current requirements and technical progress, thereby further improving the relevance and comparability of harmonised indices of consumer prices and the HPI. On the basis of the new framework established by this Regulation, work on a set of supplementary indicators on price evolution should be initiated. |
|
(7) |
This Regulation takes into account the Commission’s better regulation agenda and, in particular, the Commission communication of 8 October 2010 entitled Smart regulation in the European Union. In the statistical field, the Commission has set as a priority the simplification and improvement of the regulatory environment in statistics, as referred to in the Commission communication of 10 August 2009 on the production method of EU statistics: a vision for the next decade. |
|
(8) |
The HICP and the harmonised index of consumer prices at constant tax rates (HICP-CT) should be broken down into categories of the European classification of individual consumption according to purpose (ECOICOP). Such classification should ensure that all European statistics relating to private consumption are consistent and comparable. The ECOICOP should also be consistent with the UN COICOP, which is the international standard classifying individual consumption according to purpose, therefore the ECOICOP should be adapted to align it with changes to the UN COICOP. |
|
(9) |
The HICP is based on observed prices, which include taxes on products. Hence, inflation is affected by changes to tax rates on products. For inflation analysis and for convergence assessment in Member States, information also needs to be collected on the impact of tax changes on inflation. To this end, the HICP should additionally be calculated on the basis of constant tax rate prices. |
|
(10) |
Establishing price indices for dwellings, and in particular for owner-occupied housing (OOH), is an important step towards further improving the relevance and comparability of the HICP. The HPI is a necessary basis for compiling the OOH price index. In addition, the HPI is an important indicator in its own right. By 31 December 2018, the Commission should prepare a report addressing the suitability of the OOH price index for integration into the HICP coverage. Depending on the results of that report, the Commission should, where appropriate, submit, within a reasonable time frame, a proposal for amending this Regulation with regard to integrating the OOH price index into the HICP coverage. |
|
(11) |
Early provisional information on the monthly HICP in the form of a flash estimate is crucial for monetary policy in the euro area. Therefore, such flash estimates should be provided by the Member States whose currency is the euro. |
|
(12) |
The HICP is designed to assess price stability. It is not intended to be a cost of living index. In addition to the HICP, research on a harmonised cost of living index should be initiated. |
|
(13) |
The reference period of the harmonised indices should be updated periodically. Rules for common index reference periods of the harmonised indices and their sub-indices integrated at different points in time should be established in order to ensure that the resulting indices are comparable and relevant. |
|
(14) |
In order to enhance the gradual harmonisation of harmonised indices of consumer prices and the HPI, pilot studies should be launched to assess the feasibility of using improved basic information or applying new methodological approaches. The Commission should take the necessary actions and find the right incentives, including financial support, to encourage such pilot studies. |
|
(15) |
The Commission (Eurostat) should verify the sources and methods used by Member States to calculate harmonised indices and should monitor the implementation of the legal framework by Member States. For that purpose, the Commission (Eurostat) should maintain a regular dialogue with the Member States’ statistical authorities. |
|
(16) |
Background information is essential for assessing whether the detailed harmonised indices provided by the Member States are sufficiently comparable. In addition, transparent compilation methods and practices used in Member States help all stakeholders to understand the harmonised indices and further improve their quality. A set of rules for reporting harmonised metadata should therefore be established. |
|
(17) |
In order to ensure the quality of statistical data provided by Member States, the Commission should use the appropriate prerogatives and powers provided for in Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council (5). |
|
(18) |
In order to ensure adaptation to changes to the UN COICOP, to amend the list of items regulated by implementing acts by adding items in order to take account of technical developments in the statistical methods and based on the evaluation of pilot studies, and to modify the list of sub-indices of ECOICOP that Member States are not required to produce in order to include games of chance in the HICP and the HICP-CT, the power to adopt acts in accordance with Article 290 TFEU should be delegated to the Commission. It is of particular importance that the Commission carry out appropriate consultations during its preparatory work, including at expert level. The Commission, when preparing and drawing up delegated acts, should ensure a simultaneous, timely and appropriate transmission of relevant documents to the European Parliament and to the Council. |
|
(19) |
In order to ensure full comparability of the harmonised indices, uniform conditions are needed for the application of the ECOICOP for the purpose of the HICP and the HICP-CT; for the breakdown of the flash estimate of the HICP provided by Member States whose currency is the euro; for the breakdowns of the OOH price index and of the HPI; for the quality of weights of the harmonised indices; for improved methods based on voluntary pilot studies; for the appropriate methodology; for detailed rules on the rescaling of the harmonised indices; for the data and metadata exchange standards; for the revision of the harmonised indices and their sub-indices; and for technical quality assurance requirements regarding the content of annual standard quality reports, the deadline for providing the reports to the Commission (Eurostat) and the structure of the inventories and the deadline for providing the inventories to the Commission (Eurostat). In order to ensure such uniform conditions for the implementation of this Regulation, implementing powers should be conferred on the Commission. Those powers should be exercised in accordance with Regulation (EU) No 182/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council (6). |
|
(20) |
In adopting implementing measures and delegated acts in accordance with this Regulation, the Commission should consider, where appropriate, cost-effectiveness and ensure that those measures and acts do not impose a significant additional burden on Member States or respondents. |
|
(21) |
Since the objective of this Regulation, namely the creation of common statistical standards for harmonised indices of consumer prices and the HPI, cannot be sufficiently achieved by the Member States but can rather be better achieved at Union level, the Union may adopt measures, in accordance with the principle of subsidiarity as set out in Article 5 of the Treaty on European Union. In accordance with the principle of proportionality, as set out in that Article, this Regulation does not go beyond what is necessary in order to achieve that objective. |
|
(22) |
In the context of Article 7 of Regulation (EC) No 223/2009, the European Statistical System Committee has been asked to provide its professional guidance. |
|
(23) |
Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 should therefore be repealed, |
HAVE ADOPTED THIS REGULATION:
Article 1
Subject matter
This Regulation lays down a common framework for the development, production and dissemination of harmonised indices of consumer prices (HICP, HICP-CT, OOH price index) and of the house price index (HPI) at Union and national level.
Article 2
Definitions
For the purposes of this Regulation, the following definitions apply:
|
(1) |
‘products’ means goods and services as defined in paragraph 3.01 of Annex A to Regulation (EU) No 549/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council (7) (‘ESA 2010’); |
|
(2) |
‘consumer prices’ means the purchase prices paid by households to purchase individual products by means of monetary transactions; |
|
(3) |
‘house prices’ means the transaction prices of dwellings purchased by households; |
|
(4) |
‘purchase prices’ means the prices actually paid by purchasers for products, including any taxes less subsidies on the products, after the deduction of discounts from standard prices or charges, excluding interest or services charges added under credit arrangements and any extra charges incurred as a result of failing to pay within the period specified at the time of purchase; |
|
(5) |
‘administered prices’ means prices that are either directly set or influenced to a significant extent by the government; |
|
(6) |
‘harmonised index of consumer prices’ or ‘HICP’ means the comparable index of consumer prices produced by each Member State; |
|
(7) |
‘harmonised index of consumer prices at constant tax rates’ or ‘HICP-CT’ means the index that measures changes in consumer prices without the impact of changes in tax rates on products over the same period of time; |
|
(8) |
‘tax rate’ means a tax parameter and may be a certain percentage of the price or an absolute tax amount levied on a physical unit; |
|
(9) |
‘owner-occupied housing price index’ or ‘OOH price index’ means the index that measures changes in the transaction prices of dwellings new to the household sector and of other products that the households acquire in their role as owner-occupiers; |
|
(10) |
‘house price index’ or ‘HPI’ means the index that measures changes in the transaction prices of dwellings purchased by households; |
|
(11) |
‘sub-index of the HICP or the HICP-CT’ means the price index for any category of the European classification of individual consumption according to purpose (ECOICOP) as set out in Annex I; |
|
(12) |
‘harmonised indices’ means the HICP, the HICP-CT, the OOH price index and the HPI; |
|
(13) |
‘flash estimate of the HICP’ means an early estimate of the HICP provided by Member States whose currency is the euro that may be based on provisional information and, if necessary, appropriate modelling; |
|
(14) |
‘Laspeyres-type index’ means the price index that measures the average change in prices from the price reference period to a comparison period using expenditure shares from a period prior to the price reference period, and where the expenditure shares are adjusted to reflect the prices of the price reference period. A ‘Laspeyres-type index’ is defined as:
The price of a product is denoted by p, the price reference period is denoted by 0, and the comparison period is denoted by t. Weights (w) are expenditure shares of a period (b) prior to the price reference period, and are adjusted to reflect the prices of the price reference period 0; |
|
(15) |
‘index reference period’ means the period for which the index is set to 100 index points; |
|
(16) |
‘price reference period’ means the period to which the price of the comparison period is compared; for monthly indices, the price reference period is December of the previous year, and for quarterly indices, the price reference period is the fourth quarter of the previous year; |
|
(17) |
‘basic information’ means data covering:
|
|
(18) |
‘household’ means a household as referred to in points (a) and (b) of paragraph 2.119 of Annex A to ESA 2010, irrespective of nationality or residence status; |
|
(19) |
‘economic territory of the Member State’ means the economic territory as referred to in paragraph 2.05 of Annex A to ESA 2010, with the exception that the extraterritorial enclaves situated within the boundaries of the Member State are included and the territorial enclaves situated in the rest of the world are excluded; |
|
(20) |
‘household final monetary consumption expenditure’ means that part of final consumption expenditure incurred:
|
|
(21) |
‘significant change in the production method’ means a change that is estimated to affect the annual rate of change of a given harmonised index or part thereof in any period by more than:
|
Article 3
Compilation of the harmonised indices
1. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the harmonised indices as defined in point (12) of Article 2.
2. The harmonised indices shall be annually chain-linked Laspeyres-type indices.
3. The HICP and the HICP-CT shall be based on the price changes and weights of products included in the household final monetary consumption expenditure.
4. Neither the HICP nor the HICP-CT shall cover transactions between households, except in the case of rentals paid by tenants to private landlords, where the latter act as market producers of services purchased by households (tenants).
5. The OOH price index shall be compiled, where possible and provided that the data are available, for the 10 years preceding the entry into force of this Regulation.
6. Sub-indices of the HICP and of the HICP-CT shall be compiled for the categories of ECOICOP. The Commission shall adopt implementing acts specifying uniform conditions for the application of the ECOICOP for the purpose of the HICP and the HICP-CT. Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
7. By 31 December 2018, the Commission shall prepare a report which shall address the suitability of the OOH price index for integration into the HICP coverage. Depending on the results of the report, the Commission shall, where appropriate, submit, within a reasonable timeframe, a proposal for amending this Regulation with regard to integrating the OOH price index into the HICP coverage. If the report establishes that further methodological developments are required for the integration of the OOH price index into the HICP coverage, the Commission shall pursue the methodological work and report to the European Parliament and to the Council on that work, as appropriate.
8. The Commission shall adopt implementing acts specifying the breakdown of the flash estimate of the HICP provided by Member States whose currency is the euro. Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
9. The Commission shall adopt implementing acts specifying the breakdowns of the OOH price index and of the HPI. Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
10. Each year, Member States shall update sub-index weights for the harmonised indices. The Commission shall adopt implementing acts specifying uniform conditions for the quality of weights of the harmonised indices. Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
Article 4
Comparability of the harmonised indices
1. For the harmonised indices to be considered comparable, any differences across Member States at all levels of detail shall only reflect differences in price changes or expenditure patterns.
2. Any sub-indices of the harmonised indices that deviate from the concepts or methods of this Regulation shall be deemed comparable if they result in an index that is estimated to differ systematically by:
|
(a) |
less than or equal to 0,1 percentage points on average over one year against the previous year from an index compiled following the methodological approach of this Regulation, in the case of the HICP and the HICP-CT; |
|
(b) |
less than or equal to one percentage point on average over one year against the previous year from an index compiled following the methodological approach of this Regulation, in the case of the OOH price index and the HPI. |
Where the calculations referred to in the first subparagraph are not possible, Member States shall set out in detail the consequences of using a methodology which deviates from the concepts or methods of this Regulation.
3. The Commission shall be empowered to adopt delegated acts in accordance with Article 10 for the amendment of Annex I, in order to ensure comparability of the harmonised indices at international level in accordance with changes to the UN COICOP.
4. In order to ensure uniform conditions in producing comparable harmonised indices, and for the purposes of achieving the objectives of this Regulation, the Commission shall adopt implementing acts further specifying improved methods based on voluntary pilot studies as referred to in Article 8, and the methodology. Those implementing acts shall concern:
|
(i) |
sampling and representativity; |
|
(ii) |
collection and treatment of prices; |
|
(iii) |
replacements and quality adjustment; |
|
(iv) |
index compilation; |
|
(v) |
revisions; |
|
(vi) |
special indices; |
|
(vii) |
treatment of products in specific areas. |
The Commission shall ensure that those implementing acts do not impose a significant additional burden on the Member States or on the respondents.
Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
5. With a view to the production of the harmonised indices, in order to take account of technical developments in the statistical methods and based on the evaluation of the pilot studies referred to in Article 8(4), the Commission shall be empowered to amend, by means of delegated acts adopted in accordance with Article 10, the first subparagraph of paragraph 4 of this Article by adding items to the list set out therein, provided that such added items do not overlap with existing ones and do not change the scope or nature of harmonised indices as set out in this Regulation.
Article 5
Data requirements
1. Basic information collected by Member States for the harmonised indices and their sub-indices shall be representative at Member State level.
2. The information shall be obtained from statistical units as defined in Council Regulation (EEC) No 696/93 (8) or from other sources, provided that the comparability requirements for the harmonised indices referred to in Article 4 of this Regulation are met.
3. The statistical units that provide information on products included in the household final monetary consumption expenditure shall cooperate in the collection or provision of basic information, as required. The statistical units shall give accurate and complete basic information to the national bodies responsible for compiling the harmonised indices.
4. Upon the request of the national bodies responsible for compiling the harmonised indices, the statistical units shall provide, where available, electronic records of transactions, such as scanner data, and at the level of detail necessary in order to produce harmonised indices and to evaluate compliance with the comparability requirements and the quality of the harmonised indices.
5. The common index reference period for the harmonised indices shall be 2015. That index reference period shall be used for the full time series of all harmonised indices and their sub-indices.
6. The harmonised indices and their sub-indices shall be rescaled to a new common index reference period in the case of a major methodological change of the harmonised indices which is adopted in accordance with this Regulation, or every 10 years after the last rescaling starting from 2015. The rescaling to the new index reference period shall take effect:
|
(a) |
for monthly indices, with the index for January of the following year after the index reference period; |
|
(b) |
for quarterly indices, with the index for the first quarter of the following year after the index reference period. |
The Commission shall adopt implementing acts establishing detailed rules on the rescaling of the harmonised indices. Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
7. Member States shall not be required to produce and transmit:
|
(a) |
sub-indices of the HICP and of the HICP-CT accounting for less than one part in a thousand of the total expenditure; |
|
(b) |
sub-indices of the OOH price index and of the HPI accounting for less than one part in a hundred of the total owner-occupier housing expenditure and total purchases of dwellings, respectively. |
8. Member States shall not be required to produce the following sub-indices of ECOICOP, either because they are not included in the household final monetary consumption expenditure or because the degree of methodological harmonisation is not yet sufficient:
|
02.3 |
Narcotics; |
|
09.4.3 |
Games of chance; |
|
12.2 |
Prostitution; |
|
12.5.1 |
Life insurance; |
|
12.6.1 |
FISIM. |
The Commission shall be empowered to adopt delegated acts in accordance with Article 10 to modify the list set out in this paragraph in order to include games of chance in the HICP and the HICP-CT.
Article 6
Frequency
1. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the HICP, the HICP-CT and their respective sub-indices at monthly intervals, including those sub-indices produced at longer intervals.
2. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the OOH price index and the HPI at quarterly intervals. They may be provided at monthly intervals on a voluntary basis.
3. Member States shall not be required to produce sub-indices at monthly or quarterly intervals where less frequent data collection fulfils the comparability requirements of Article 4. Member States shall inform the Commission (Eurostat) of the ECOICOP, the OOH price index and the HPI categories for which they intend to collect data at intervals less frequent than monthly, in the case of ECOICOP categories, and quarterly, in the case of the OOH price index and the HPI categories.
4. Each year, Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with updated sub-index weights for the harmonised indices.
Article 7
Deadlines, exchange standards and revisions
1. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the harmonised indices and all sub-indices by no later than:
|
(a) |
15 calendar days, for the February to December indices, and 20 calendar days, for the January indices, after the end of the month for which the indices are calculated; and |
|
(b) |
85 calendar days after the end of the quarter for which the indices are calculated. |
2. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the updated weights by no later than:
|
(a) |
13 February each year for the monthly indices; |
|
(b) |
15 June each year for the quarterly indices. |
3. Member States whose currency is the euro shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the flash estimate of the HICP no later than the penultimate calendar day of the month to which the flash estimate refers.
4. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with the data and metadata required by this Regulation in accordance with data and metadata exchange standards.
5. Harmonised indices and their sub-indices that have already been published may be revised.
6. The Commission shall adopt implementing acts specifying in detail the data and metadata exchange standards referred to in paragraph 4, and the uniform conditions for the revision of harmonised indices and their sub-indices as referred to in paragraph 5. Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
Article 8
Pilot studies
1. Whenever improved basic information is required for the compilation of the harmonised indices, or when the need for improved comparability of the harmonised indices is identified in the methods referred to in Article 4(4), the Commission (Eurostat) may launch pilot studies, to be carried out on a voluntary basis by Member States.
2. The general budget of the Union shall, where appropriate, contribute to the financing of such pilot studies.
3. The pilot studies shall assess the feasibility of obtaining improved basic information or adopting new methodological approaches.
4. The results of the pilot studies shall be evaluated by the Commission (Eurostat) in close cooperation with Member States and the main users of the harmonised indices, taking into account the benefits of having improved basic information or new methodological approaches relative to the additional costs of production of harmonised indices.
5. By 31 December 2020 and every five years thereafter, the Commission shall submit a report to the European Parliament and the Council evaluating, if applicable, the main findings of the pilot studies.
Article 9
Quality assurance
1. Member States shall ensure the quality of the harmonised indices provided. For the purposes of this Regulation, the standard quality criteria set out in Article 12(1) of Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 shall apply.
2. Member States shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with:
|
(a) |
annual standard quality reports covering the quality criteria referred to in Article 12(1) of Regulation (EC) No 223/2009; |
|
(b) |
annually updated inventories containing details of data sources, definitions and methods used; |
|
(c) |
further related information at the level of detail necessary to evaluate compliance with the comparability requirements and the quality of the harmonised indices, if requested by the Commission (Eurostat). |
3. If a Member State intends to introduce a significant change in the production methods of the harmonised indices or a part thereof, the Member State shall inform the Commission (Eurostat) thereof at the latest three months before any such change would enter into force. The Member State shall provide the Commission (Eurostat) with a quantification of the impact of the change.
4. The Commission shall adopt implementing acts establishing technical quality assurance requirements regarding the content of the annual standard quality reports, the deadline for providing the reports to the Commission (Eurostat) and the structure of the inventories and the deadline for providing the inventories to the Commission (Eurostat). Those implementing acts shall be adopted in accordance with the examination procedure referred to in Article 11(2).
Article 10
Exercise of the delegation
1. The power to adopt delegated acts is conferred on the Commission subject to the conditions laid down in this Article.
2. When exercising the power delegated in Articles 4(3), 4(5) and 5(8), the Commission shall ensure that the delegated acts do not impose a significant additional burden on Member States or on the respondents.
In addition, the Commission shall duly justify the actions provided for in those delegated acts, considering, where appropriate, cost-effectiveness, including the burden on respondents and the production costs in accordance with Article 14(3) of Regulation (EC) No 223/2009.
The Commission shall follow its usual practice and carry out consultations with experts, including Member States’ experts, before adopting those delegated acts.
3. The power to adopt delegated acts referred to in Articles 4(3), 4(5) and 5(8) shall be conferred on the Commission for a period of five years as from 13 June 2016. The Commission shall draw up a report in respect of the delegation of power no later than nine months before the end of the five-year period. The delegation of power shall be tacitly extended for periods of an identical duration, unless the European Parliament or the Council opposes such extension no later than three months before the end of each period.
4. The delegation of power referred to in Articles 4(3), 4(5) and 5(8) may be revoked at any time by the European Parliament or by the Council. A decision to revoke shall put an end to the delegation of the power specified in that decision. It shall take effect the day following the publication of the decision in the Official Journal of the European Union or at a later date specified therein. It shall not affect the validity of any delegated acts already in force.
5. As soon as it adopts a delegated act, the Commission shall notify it simultaneously to the European Parliament and to the Council.
6. A delegated act adopted pursuant to Articles 4(3), 4(5) and 5(8) shall enter into force only if no objection has been expressed either by the European Parliament or the Council within a period of three months of notification of that act to the European Parliament and the Council or if, before the expiry of that period, the European Parliament and the Council have both informed the Commission that they will not object. That period shall be extended by three months at the initiative of the European Parliament or of the Council.
Article 11
Committee procedure
1. The Commission shall be assisted by the European Statistical System Committee established by Regulation (EC) No 223/2009. That Committee shall be a committee within the meaning of Regulation (EU) No 182/2011.
2. Where reference is made to this paragraph, Article 5 of Regulation (EU) No 182/2011 shall apply.
Article 12
Repeal
1. Without prejudice to paragraph 2, Member States shall continue to provide the harmonised indices in accordance with Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 up to the transmission of data relating to 2016.
2. Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 is repealed with effect from 1 January 2017.
References to the repealed Regulation shall be construed as references to this Regulation and shall be read in accordance with the correlation table set out in Annex II.
3. When first adopting the implementing acts referred to in Articles 3(6), 3(9), 3(10), 4(4), 5(6) and 7(6), the Commission shall, to the extent compatible with this Regulation, incorporate the relevant provisions of Commission Regulation (EC) No 1749/96 (9), Commission Regulation (EC) No 2214/96 (10), Council Regulation (EC) No 1687/98 (11), Commission Regulation (EC) No 2646/98 (12), Commission Regulation (EC) No 1617/1999 (13), Council Regulation (EC) No 2166/1999 (14), Commission Regulation (EC) No 2601/2000 (15), Commission Regulation (EC) No 2602/2000 (16), Commission Regulation (EC) No 1920/2001 (17), Commission Regulation (EC) No 1921/2001 (18), Commission Regulation (EC) No 1708/2005 (19), Council Regulation (EC) No 701/2006 (20), Commission Regulation (EC) No 330/2009 (21), Commission Regulation (EU) No 1114/2010 (22) and Commission Regulation (EU) No 93/2013 (23) adopted on the basis of Regulation (EC) No 2494/95, whilst reducing, to the extent appropriate, the overall number of implementing acts. The Regulations adopted on the basis of Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 shall remain applicable for a transitional period. That transitional period shall end on the date of application of the implementing acts first adopted on the basis of Articles 3(6), 3(9), 3(10), 4(4), 5(6) and 7(6) of this Regulation, which shall be the same date for all of those implementing acts.
Article 13
Entry into force
This Regulation shall enter into force on the twentieth day following that of its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.
It shall apply for the first time to data relating to January 2017.
This Regulation shall be binding in its entirety and directly applicable in all Member States.
Done at Strasbourg, 11 May 2016.
For the European Parliament
The President
M. SCHULZ
For the Council
The President
J.A. HENNIS-PLASSCHAERT
(1) OJ C 175, 29.5.2015, p. 2.
(2) Position of the European Parliament of 8 March 2016 (not yet published in the Official Journal) and decision of the Council of 21 April 2016.
(3) Regulation (EU) No 1176/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 November 2011 on the prevention and correction of macroeconomic imbalances (OJ L 306, 23.11.2011, p. 25).
(4) Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 of 23 October 1995 concerning harmonised indices of consumer prices (OJ L 257, 27.10.1995, p. 1).
(5) Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 March 2009 on European Statistics and repealing Regulation (EC, Euratom) No 1101/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the transmission of data subject to statistical confidentiality to the Statistical Office of the European Communities, Council Regulation (EC) No 322/97 on Community Statistics, and Council Decision 89/382/EEC, Euratom establishing a Committee on the Statistical Programmes of the European Communities (OJ L 87, 31.3.2009, p. 164).
(6) Regulation (EU) No 182/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 February 2011 laying down the rules and general principles concerning mechanisms for control by Member States of the Commission’s exercise of implementing powers (OJ L 55, 28.2.2011, p. 13).
(7) Regulation (EU) No 549/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2013 on the European system of national and regional accounts in the European Union (OJ L 174, 26.6.2013, p. 1).
(8) Council Regulation (EEC) No 696/93 of 15 March 1993 on the statistical units for the observation and analysis of the production system in the Community (OJ L 76, 30.3.1993, p. 1).
(9) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1749/96 of 9 September 1996 on initial implementing measures for Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 concerning harmonized indices of consumer prices (OJ L 229, 10.9.1996, p. 3).
(10) Commission Regulation (EC) No 2214/96 of 20 November 1996 concerning harmonized indices of consumer prices: transmission and dissemination of sub-indices of the HICP (OJ L 296, 21.11.1996, p. 8).
(11) Council Regulation (EC) No 1687/98 of 20 July 1998 amending Commission Regulation (EC) No 1749/96 concerning the coverage of goods and services of the harmonised index of consumer prices (OJ L 214, 31.7.1998, p. 12).
(12) Commission Regulation (EC) No 2646/98 of 9 December 1998 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for the treatment of tariffs in the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (OJ L 335, 10.12.1998, p. 30).
(13) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1617/1999 of 23 July 1999 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 — as regards minimum standards for the treatment of insurance in the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices and modifying Commission Regulation (EC) No 2214/96 (OJ L 192, 24.7.1999, p. 9).
(14) Council Regulation (EC) No 2166/1999 of 8 October 1999 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for the treatment of products in the health, education and social protection sectors in the Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (OJ L 266, 14.10.1999, p. 1).
(15) Commission Regulation (EC) No 2601/2000 of 17 November 2000 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards the timing of entering purchaser prices into the Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (OJ L 300, 29.11.2000, p. 14).
(16) Commission Regulation (EC) No 2602/2000 of 17 November 2000 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for the treatment of price reductions in the Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (OJ L 300, 29.11.2000, p. 16).
(17) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1920/2001 of 28 September 2001 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for the treatment of service charges proportional to transaction values in the harmonised index of consumer prices and amending Regulation (EC) No 2214/96 (OJ L 261, 29.9.2001, p. 46).
(18) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1921/2001 of 28 September 2001 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for revisions of the harmonised index of consumer prices and amending Regulation (EC) No 2602/2000 (OJ L 261, 29.9.2001, p. 49).
(19) Commission Regulation (EC) No 1708/2005 of 19 October 2005 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards the common index reference period for the harmonised index of consumer prices, and amending Regulation (EC) No 2214/96 (OJ L 274, 20.10.2005, p. 9).
(20) Council Regulation (EC) No 701/2006 of 25 April 2006 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards the temporal coverage of price collection in the harmonised index of consumer prices (OJ L 122, 9.5.2006, p. 3).
(21) Commission Regulation (EC) No 330/2009 of 22 April 2009 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for the treatment of seasonal products in the Harmonised Indices of Consumer Prices (HICP) (OJ L 103, 23.4.2009, p. 6).
(22) Commission Regulation (EU) No 1114/2010 of 1 December 2010 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 as regards minimum standards for the quality of HICP weightings and repealing Commission Regulation (EC) No 2454/97 (OJ L 316, 2.12.2010, p. 4).
(23) Commission Regulation (EU) No 93/2013 of 1 February 2013 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 concerning harmonised indices of consumer prices, as regards establishing owner-occupied housing price indices (OJ L 33, 2.2.2013, p. 14).
ANNEX I
EUROPEAN CLASSIFICATION OF INDIVIDUAL CONSUMPTION ACCORDING TO PURPOSE (ECOICOP)
|
01 |
FOOD AND NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES |
|
01.1 |
Food |
|
01.1.1 |
Bread and cereals |
|
01.1.1.1 |
Rice |
|
01.1.1.2 |
Flours and other cereals |
|
01.1.1.3 |
Bread |
|
01.1.1.4 |
Other bakery products |
|
01.1.1.5 |
Pizza and quiche |
|
01.1.1.6 |
Pasta products and couscous |
|
01.1.1.7 |
Breakfast cereals |
|
01.1.1.8 |
Other cereal products |
|
01.1.2 |
Meat |
|
01.1.2.1 |
Beef and veal |
|
01.1.2.2 |
Pork |
|
01.1.2.3 |
Lamb and goat |
|
01.1.2.4 |
Poultry |
|
01.1.2.5 |
Other meats |
|
01.1.2.6 |
Edible offal |
|
01.1.2.7 |
Dried, salted or smoked meat |
|
01.1.2.8 |
Other meat preparations |
|
01.1.3 |
Fish and seafood |
|
01.1.3.1 |
Fresh or chilled fish |
|
01.1.3.2 |
Frozen fish |
|
01.1.3.3 |
Fresh or chilled seafood |
|
01.1.3.4 |
Frozen seafood |
|
01.1.3.5 |
Dried, smoked or salted fish and seafood |
|
01.1.3.6 |
Other preserved or processed fish and seafood-based preparations |
|
01.1.4 |
Milk, cheese and eggs |
|
01.1.4.1 |
Fresh whole milk |
|
01.1.4.2 |
Fresh low fat milk |
|
01.1.4.3 |
Preserved milk |
|
01.1.4.4 |
Yoghurt |
|
01.1.4.5 |
Cheese and curd |
|
01.1.4.6 |
Other milk products |
|
01.1.4.7 |
Eggs |
|
01.1.5 |
Oils and fats |
|
01.1.5.1 |
Butter |
|
01.1.5.2 |
Margarine and other vegetable fats |
|
01.1.5.3 |
Olive oil |
|
01.1.5.4 |
Other edible oils |
|
01.1.5.5 |
Other edible animal fats |
|
01.1.6 |
Fruit |
|
01.1.6.1 |
Fresh or chilled fruit |
|
01.1.6.2 |
Frozen fruit |
|
01.1.6.3 |
Dried fruit and nuts |
|
01.1.6.4 |
Preserved fruit and fruit-based products |
|
01.1.7 |
Vegetables |
|
01.1.7.1 |
Fresh or chilled vegetables other than potatoes and other tubers |
|
01.1.7.2 |
Frozen vegetables other than potatoes and other tubers |
|
01.1.7.3 |
Dried vegetables, other preserved or processed vegetables |
|
01.1.7.4 |
Potatoes |
|
01.1.7.5 |
Crisps |
|
01.1.7.6 |
Other tubers and products of tuber vegetables |
|
01.1.8 |
Sugar, jam, honey, chocolate and confectionery |
|
01.1.8.1 |
Sugar |
|
01.1.8.2 |
Jams, marmalades and honey |
|
01.1.8.3 |
Chocolate |
|
01.1.8.4 |
Confectionery products |
|
01.1.8.5 |
Edible ices and ice cream |
|
01.1.8.6 |
Artificial sugar substitutes |
|
01.1.9 |
Food products n.e.c. |
|
01.1.9.1 |
Sauces, condiments |
|
01.1.9.2 |
Salt, spices and culinary herbs |
|
01.1.9.3 |
Baby food |
|
01.1.9.4 |
Ready-made meals |
|
01.1.9.9 |
Other food products n.e.c. |
|
01.2 |
Non-alcoholic beverages |
|
01.2.1 |
Coffee, tea and cocoa |
|
01.2.1.1 |
Coffee |
|
01.2.1.2 |
Tea |
|
01.2.1.3 |
Cocoa and powdered chocolate |
|
01.2.2 |
Mineral waters, soft drinks, fruit and vegetable juices |
|
01.2.2.1 |
Mineral or spring waters |
|
01.2.2.2 |
Soft drinks |
|
01.2.2.3 |
Fruit and vegetable juices |
|
02 |
ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, TOBACCO AND NARCOTICS |
|
02.1 |
Alcoholic beverages |
|
02.1.1 |
Spirits |
|
02.1.1.1 |
Spirits and liqueurs |
|
02.1.1.2 |
Alcoholic soft drinks |
|
02.1.2 |
Wine |
|
02.1.2.1 |
Wine from grapes |
|
02.1.2.2 |
Wine from other fruits |
|
02.1.2.3 |
Fortified wines |
|
02.1.2.4 |
Wine-based drinks |
|
02.1.3 |
Beer |
|
02.1.3.1 |
Lager beer |
|
02.1.3.2 |
Other alcoholic beer |
|
02.1.3.3 |
Low and non-alcoholic beer |
|
02.1.3.4 |
Beer-based drinks |
|
02.2 |
Tobacco |
|
02.2.0 |
Tobacco |
|
02.2.0.1 |
Cigarettes |
|
02.2.0.2 |
Cigars |
|
02.2.0.3 |
Other tobacco products |
|
02.3 |
Narcotics |
|
02.3.0 |
Narcotics |
|
02.3.0.0 |
Narcotics |
|
03 |
CLOTHING AND FOOTWEAR |
|
03.1 |
Clothing |
|
03.1.1 |
Clothing materials |
|
03.1.1.0 |
Clothing materials |
|
03.1.2 |
Garments |
|
03.1.2.1 |
Garments for men |
|
03.1.2.2 |
Garments for women |
|
03.1.2.3 |
Garments for infants (0 to 2 years) and children (3 to 13 years) |
|
03.1.3 |
Other articles of clothing and clothing accessories |
|
03.1.3.1 |
Other articles of clothing |
|
03.1.3.2 |
Clothing accessories |
|
03.1.4 |
Cleaning, repair and hire of clothing |
|
03.1.4.1 |
Cleaning of clothing |
|
03.1.4.2 |
Repair and hire of clothing |
|
03.2 |
Footwear |
|
03.2.1 |
Shoes and other footwear |
|
03.2.1.1 |
Footwear for men |
|
03.2.1.2 |
Footwear for women |
|
03.2.1.3 |
Footwear for infants and children |
|
03.2.2 |
Repair and hire of footwear |
|
03.2.2.0 |
Repair and hire of footwear |
|
04 |
HOUSING, WATER, ELECTRICITY, GAS AND OTHER FUELS |
|
04.1 |
Actual rentals for housing |
|
04.1.1 |
Actual rentals paid by tenants |
|
04.1.1.0 |
Actual rentals paid by tenants |
|
04.1.2 |
Other actual rentals |
|
04.1.2.1 |
Actual rentals paid by tenants for secondary residences |
|
04.1.2.2 |
Garage rentals and other rentals paid by tenants |
|
04.2 |
Imputed rentals for housing |
|
04.2.1 |
Imputed rentals of owner-occupiers |
|
04.2.1.0 |
Imputed rentals of owner-occupiers |
|
04.2.2 |
Other imputed rentals |
|
04.2.2.0 |
Other imputed rentals |
|
04.3 |
Maintenance and repair of the dwelling |
|
04.3.1 |
Materials for the maintenance and repair of the dwelling |
|
04.3.1.0 |
Materials for the maintenance and repair of the dwelling |
|
04.3.2 |
Services for the maintenance and repair of the dwelling |
|
04.3.2.1 |
Services of plumbers |
|
04.3.2.2 |
Services of electricians |
|
04.3.2.3 |
Maintenance services for heating systems |
|
04.3.2.4 |
Services of painters |
|
04.3.2.5 |
Services of carpenters |
|
04.3.2.9 |
Other services for maintenance and repair of the dwelling |
|
04.4 |
Water supply and miscellaneous services relating to the dwelling |
|
04.4.1 |
Water supply |
|
04.4.1.0 |
Water supply |
|
04.4.2 |
Refuse collection |
|
04.4.2.0 |
Refuse collection |
|
04.4.3 |
Sewage collection |
|
04.4.3.0 |
Sewage collection |
|
04.4.4 |
Other services relating to the dwelling n.e.c. |
|
04.4.4.1 |
Maintenance charges in multi-occupied buildings |
|
04.4.4.2 |
Security services |
|
04.4.4.9 |
Other services related to dwelling |
|
04.5 |
Electricity, gas and other fuels |
|
04.5.1 |
Electricity |
|
04.5.1.0 |
Electricity |
|
04.5.2 |
Gas |
|
04.5.2.1 |
Natural gas and town gas |
|
04.5.2.2 |
Liquefied hydrocarbons (butane, propane, etc.) |
|
04.5.3 |
Liquid fuels |
|
04.5.3.0 |
Liquid fuels |
|
04.5.4 |
Solid fuels |
|
04.5.4.1 |
Coal |
|
04.5.4.9 |
Other solid fuels |
|
04.5.5 |
Heat energy |
|
04.5.5.0 |
Heat energy |
|
05 |
FURNISHINGS, HOUSEHOLD EQUIPMENT AND ROUTINE HOUSEHOLD MAINTENANCE |
|
05.1 |
Furniture and furnishings, carpets and other floor coverings |
|
05.1.1 |
Furniture and furnishings |
|
05.1.1.1 |
Household furniture |
|
05.1.1.2 |
Garden furniture |
|
05.1.1.3 |
Lighting equipment |
|
05.1.1.9 |
Other furniture and furnishings |
|
05.1.2 |
Carpets and other floor coverings |
|
05.1.2.1 |
Carpets and rugs |
|
05.1.2.2 |
Other floor coverings |
|
05.1.2.3 |
Services of laying of fitted carpets and floor coverings |
|
05.1.3 |
Repair of furniture, furnishings and floor coverings |
|
05.1.3.0 |
Repair of furniture, furnishings and floor coverings |
|
05.2 |
Household textiles |
|
05.2.0 |
Household textiles |
|
05.2.0.1 |
Furnishing fabrics and curtains |
|
05.2.0.2 |
Bed linen |
|
05.2.0.3 |
Table linen and bathroom linen |
|
05.2.0.4 |
Repair of household textiles |
|
05.2.0.9 |
Other household textiles |
|
05.3 |
Household appliances |
|
05.3.1 |
Major household appliances whether electric or not |
|
05.3.1.1 |
Refrigerators, freezers and fridge-freezers |
|
05.3.1.2 |
Clothes washing machines, clothes drying machines and dish washing machines |
|
05.3.1.3 |
Cookers |
|
05.3.1.4 |
Heaters, air conditioners |
|
05.3.1.5 |
Cleaning equipment |
|
05.3.1.9 |
Other major household appliances |
|
05.3.2 |
Small electric household appliances |
|
05.3.2.1 |
Food processing appliances |
|
05.3.2.2 |
Coffee machines, tea makers and similar appliances |
|
05.3.2.3 |
Irons |
|
05.3.2.4 |
Toasters and grills |
|
05.3.2.9 |
Other small electric household appliances |
|
05.3.3 |
Repair of household appliances |
|
05.3.3.0 |
Repair of household appliances |
|
05.4 |
Glassware, tableware and household utensils |
|
05.4.0 |
Glassware, tableware and household utensils |
|
05.4.0.1 |
Glassware, crystal-ware, ceramic ware and chinaware |
|
05.4.0.2 |
Cutlery, flatware and silverware |
|
05.4.0.3 |
Non-electric kitchen utensils and articles |
|
05.4.0.4 |
Repair of glassware, tableware and household utensils |
|
05.5 |
Tools and equipment for house and garden |
|
05.5.1 |
Major tools and equipment |
|
05.5.1.1 |
Motorised major tools and equipment |
|
05.5.1.2 |
Repair, leasing and rental of major tools and equipment |
|
05.5.2 |
Small tools and miscellaneous accessories |
|
05.5.2.1 |
Non-motorised small tools |
|
05.5.2.2 |
Miscellaneous small tool accessories |
|
05.5.2.3 |
Repair of non-motorised small tools and miscellaneous accessories |
|
05.6 |
Goods and services for routine household maintenance |
|
05.6.1 |
Non-durable household goods |
|
05.6.1.1 |
Cleaning and maintenance products |
|
05.6.1.2 |
Other non-durable small household articles |
|
05.6.2 |
Domestic services and household services |
|
05.6.2.1 |
Domestic services by paid staff |
|
05.6.2.2 |
Cleaning services |
|
05.6.2.3 |
Hire of furniture and furnishings |
|
05.6.2.9 |
Other domestic services and household services |
|
06 |
HEALTH |
|
06.1 |
Medical products, appliances and equipment |
|
06.1.1 |
Pharmaceutical products |
|
06.1.1.0 |
Pharmaceutical products |
|
06.1.2 |
Other medical products |
|
06.1.2.1 |
Pregnancy tests and mechanical contraceptive devices |
|
06.1.2.9 |
Other medical products n.e.c. |
|
06.1.3 |
Therapeutic appliances and equipment |
|
06.1.3.1 |
Corrective eye-glasses and contact lenses |
|
06.1.3.2 |
Hearing aids |
|
06.1.3.3 |
Repair of therapeutic appliances and equipment |
|
06.1.3.9 |
Other therapeutic appliances and equipment |
|
06.2 |
Out-patient services |
|
06.2.1 |
Medical services |
|
06.2.1.1 |
General practice |
|
06.2.1.2 |
Specialist practice |
|
06.2.2 |
Dental services |
|
06.2.2.0 |
Dental services |
|
06.2.3 |
Paramedical services |
|
06.2.3.1 |
Services of medical analysis laboratories and X-ray centres |
|
06.2.3.2 |
Thermal-baths, corrective-gymnastic therapy, ambulance services and hire of therapeutic equipment |
|
06.2.3.9 |
Other paramedical services |
|
06.3 |
Hospital services |
|
06.3.0 |
Hospital services |
|
06.3.0.0 |
Hospital services |
|
07 |
TRANSPORT |
|
07.1 |
Purchase of vehicles |
|
07.1.1 |
Motor cars |
|
07.1.1.1 |
New motor cars |
|
07.1.1.2 |
Second-hand motor cars |
|
07.1.2 |
Motor cycles |
|
07.1.2.0 |
Motor cycles |
|
07.1.3 |
Bicycles |
|
07.1.3.0 |
Bicycles |
|
07.1.4 |
Animal drawn vehicles |
|
07.1.4.0 |
Animal drawn vehicles |
|
07.2 |
Operation of personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.1 |
Spare parts and accessories for personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.1.1 |
Tyres |
|
07.2.1.2 |
Spare parts for personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.1.3 |
Accessories for personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.2 |
Fuels and lubricants for personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.2.1 |
Diesel |
|
07.2.2.2 |
Petrol |
|
07.2.2.3 |
Other fuels for personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.2.4 |
Lubricants |
|
07.2.3 |
Maintenance and repair of personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.3.0 |
Maintenance and repair of personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.4 |
Other services in respect of personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.4.1 |
Hire of garages, parking spaces and personal transport equipment |
|
07.2.4.2 |
Toll facilities and parking meters |
|
07.2.4.3 |
Driving lessons, tests, licences and road worthiness tests |
|
07.3 |
Transport services |
|
07.3.1 |
Passenger transport by railway |
|
07.3.1.1 |
Passenger transport by train |
|
07.3.1.2 |
Passenger transport by underground and tram |
|
07.3.2 |
Passenger transport by road |
|
07.3.2.1 |
Passenger transport by bus and coach |
|
07.3.2.2 |
Passenger transport by taxi and hired car with driver |
|
07.3.3 |
Passenger transport by air |
|
07.3.3.1 |
Domestic flights |
|
07.3.3.2 |
International flights |
|
07.3.4 |
Passenger transport by sea and inland waterway |
|
07.3.4.1 |
Passenger transport by sea |
|
07.3.4.2 |
Passenger transport by inland waterway |
|
07.3.5 |
Combined passenger transport |
|
07.3.5.0 |
Combined passenger transport |
|
07.3.6 |
Other purchased transport services |
|
07.3.6.1 |
Funicular, cable-car and chair-lift transport |
|
07.3.6.2 |
Removal and storage services |
|
07.3.6.9 |
Other purchased transport services n.e.c. |
|
08 |
COMMUNICATION |
|
08.1 |
Postal services |
|
08.1.0 |
Postal services |
|
08.1.0.1 |
Letter handling services |
|
08.1.0.9 |
Other postal services |
|
08.2 |
Telephone and telefax equipment |
|
08.2.0 |
Telephone and telefax equipment |
|
08.2.0.1 |
Fixed telephone equipment |
|
08.2.0.2 |
Mobile telephone equipment |
|
08.2.0.3 |
Other equipment of telephone and telefax equipment |
|
08.2.0.4 |
Repair of telephone or telefax equipment |
|
08.3 |
Telephone and telefax services |
|
08.3.0 |
Telephone and telefax services |
|
08.3.0.1 |
Wired telephone services |
|
08.3.0.2 |
Wireless telephone services |
|
08.3.0.3 |
Internet access provision services |
|
08.3.0.4 |
Bundled telecommunication services |
|
08.3.0.5 |
Other information transmission services |
|
09 |
RECREATION AND CULTURE |
|
09.1 |
Audiovisual, photographic and information processing equipment |
|
09.1.1 |
Equipment for the reception, recording and reproduction of sound and picture |
|
09.1.1.1 |
Equipment for the reception, recording and reproduction of sound |
|
09.1.1.2 |
Equipment for the reception, recording and reproduction of sound and vision |
|
09.1.1.3 |
Portable sound and vision devices |
|
09.1.1.9 |
Other equipment for the reception, recording and reproduction of sound and picture |
|
09.1.2 |
Photographic and cinematographic equipment and optical instruments |
|
09.1.2.1 |
Cameras |
|
09.1.2.2 |
Accessories for photographic and cinematographic equipment |
|
09.1.2.3 |
Optical instruments |
|
09.1.3 |
Information processing equipment |
|
09.1.3.1 |
Personal computers |
|
09.1.3.2 |
Accessories for information processing equipment |
|
09.1.3.3 |
Software |
|
09.1.3.4 |
Calculators and other information processing equipment |
|
09.1.4 |
Recording media |
|
09.1.4.1 |
Pre-recorded recording media |
|
09.1.4.2 |
Unrecorded recording media |
|
09.1.4.9 |
Other recording media |
|
09.1.5 |
Repair of audiovisual, photographic and information processing equipment |
|
09.1.5.0 |
Repair of audiovisual, photographic and information processing equipment |
|
09.2 |
Other major durables for recreation and culture |
|
09.2.1 |
Major durables for outdoor recreation |
|
09.2.1.1 |
Camper vans, caravans and trailers |
|
09.2.1.2 |
Aeroplanes, microlight aircraft, gliders, hang-gliders and hot-air balloons |
|
09.2.1.3 |
Boats, outboard motors and fitting out of boats |
|
09.2.1.4 |
Horses, ponies and accessories |
|
09.2.1.5 |
Major items for games and sport |
|
09.2.2 |
Musical instruments and major durables for indoor recreation |
|
09.2.2.1 |
Musical instruments |
|
09.2.2.2 |
Major durables for indoor recreation |
|
09.2.3 |
Maintenance and repair of other major durables for recreation and culture |
|
09.2.3.0 |
Maintenance and repair of other major durables for recreation and culture |
|
09.3 |
Other recreational items and equipment, gardens and pets |
|
09.3.1 |
Games, toys and hobbies |
|
09.3.1.1 |
Games and hobbies |
|
09.3.1.2 |
Toys and celebration articles |
|
09.3.2 |
Equipment for sport, camping and open-air recreation |
|
09.3.2.1 |
Equipment for sport |
|
09.3.2.2 |
Equipment for camping and open-air recreation |
|
09.3.2.3 |
Repair of equipment for sport, camping and open-air recreation |
|
09.3.3 |
Gardens, plants and flowers |
|
09.3.3.1 |
Garden products |
|
09.3.3.2 |
Plants and flowers |
|
09.3.4 |
Pets and related products |
|
09.3.4.1 |
Purchase of pets |
|
09.3.4.2 |
Products for pets |
|
09.3.5 |
Veterinary and other services for pets |
|
09.3.5.0 |
Veterinary and other services for pets |
|
09.4 |
Recreational and cultural services |
|
09.4.1 |
Recreational and sporting services |
|
09.4.1.1 |
Recreational and sporting services — Attendance |
|
09.4.1.2 |
Recreational and sporting services — Participation |
|
09.4.2 |
Cultural services |
|
09.4.2.1 |
Cinemas, theatres, concerts |
|
09.4.2.2 |
Museums, libraries, zoological gardens |
|
09.4.2.3 |
Television and radio licence fees, subscriptions |
|
09.4.2.4 |
Hire of equipment and accessories for culture |
|
09.4.2.5 |
Photographic services |
|
09.4.2.9 |
Other cultural services |
|
09.4.3 |
Games of chance |
|
09.4.3.0 |
Games of chance |
|
09.5 |
Newspapers, books and stationery |
|
09.5.1 |
Books |
|
09.5.1.1 |
Fiction books |
|
09.5.1.2 |
Educational text books |
|
09.5.1.3 |
Other non-fiction books |
|
09.5.1.4 |
Binding services and E-book downloads |
|
09.5.2 |
Newspapers and periodicals |
|
09.5.2.1 |
Newspapers |
|
09.5.2.2 |
Magazines and periodicals |
|
09.5.3 |
Miscellaneous printed matter |
|
09.5.3.0 |
Miscellaneous printed matter |
|
09.5.4 |
Stationery and drawing materials |
|
09.5.4.1 |
Paper products |
|
09.5.4.9 |
Other stationery and drawing materials |
|
09.6 |
Package holidays |
|
09.6.0 |
Package holidays |
|
09.6.0.1 |
Package domestic holidays |
|
09.6.0.2 |
Package international holidays |
|
10 |
EDUCATION |
|
10.1 |
Pre-primary and primary education |
|
10.1.0 |
Pre-primary and primary education |
|
10.1.0.1 |
Pre-primary education (ISCED-97 level 0) |
|
10.1.0.2 |
Primary education (ISCED-97 level 1) |
|
10.2 |
Secondary education |
|
10.2.0 |
Secondary education |
|
10.2.0.0 |
Secondary education |
|
10.3 |
Post-secondary non-tertiary education |
|
10.3.0 |
Post-secondary non-tertiary education |
|
10.3.0.0 |
Post-secondary non-tertiary education (ISCED-97 level 4) |
|
10.4 |
Tertiary education |
|
10.4.0 |
Tertiary education |
|
10.4.0.0 |
Tertiary education |
|
10.5 |
Education not definable by level |
|
10.5.0 |
Education not definable by level |
|
10.5.0.0 |
Education not definable by level |
|
11 |
RESTAURANTS AND HOTELS |
|
11.1 |
Catering services |
|
11.1.1 |
Restaurants, cafés and the like |
|
11.1.1.1 |
Restaurants, cafés and dancing establishments |
|
11.1.1.2 |
Fast food and take away food services |
|
11.1.2 |
Canteens |
|
11.1.2.0 |
Canteens |
|
11.2 |
Accommodation services |
|
11.2.0 |
Accommodation services |
|
11.2.0.1 |
Hotels, motels, inns and similar accommodation services |
|
11.2.0.2 |
Holiday centres, camping sites, youth hostels and similar accommodation services |
|
11.2.0.3 |
Accommodation services of other establishments |
|
12 |
MISCELLANEOUS GOODS AND SERVICES |
|
12.1 |
Personal care |
|
12.1.1 |
Hairdressing salons and personal grooming establishments |
|
12.1.1.1 |
Hairdressing for men and children |
|
12.1.1.2 |
Hairdressing for women |
|
12.1.1.3 |
Personal grooming treatments |
|
12.1.2 |
Electric appliances for personal care |
|
12.1.2.1 |
Electric appliances for personal care |
|
12.1.2.2 |
Repair of electric appliances for personal care |
|
12.1.3 |
Other appliances, articles and products for personal care |
|
12.1.3.1 |
Non-electrical appliances |
|
12.1.3.2 |
Articles for personal hygiene and wellness, esoteric products and beauty products |
|
12.2 |
Prostitution |
|
12.2.0 |
Prostitution |
|
12.2.0.0 |
Prostitution |
|
12.3 |
Personal effects n.e.c. |
|
12.3.1 |
Jewellery, clocks and watches |
|
12.3.1.1 |
Jewellery |
|
12.3.1.2 |
Clocks and watches |
|
12.3.1.3 |
Repair of jewellery, clocks and watches |
|
12.3.2 |
Other personal effects |
|
12.3.2.1 |
Travel goods |
|
12.3.2.2 |
Articles for babies |
|
12.3.2.3 |
Repair of other personal effects |
|
12.3.2.9 |
Other personal effects n.e.c. |
|
12.4 |
Social protection |
|
12.4.0 |
Social protection |
|
12.4.0.1 |
Child care services |
|
12.4.0.2 |
Retirement homes for elderly persons and residences for disabled persons |
|
12.4.0.3 |
Services to maintain people in their private homes |
|
12.4.0.4 |
Counselling |
|
12.5 |
Insurance |
|
12.5.1 |
Life insurance |
|
12.5.1.0 |
Life insurance |
|
12.5.2 |
Insurance connected with the dwelling |
|
12.5.2.0 |
Insurance connected with the dwelling |
|
12.5.3 |
Insurance connected with health |
|
12.5.3.1 |
Public insurance connected with health |
|
12.5.3.2 |
Private insurance connected with health |
|
12.5.4 |
Insurance connected with transport |
|
12.5.4.1 |
Motor vehicle insurance |
|
12.5.4.2 |
Travel insurance |
|
12.5.5 |
Other insurance |
|
12.5.5.0 |
Other insurance |
|
12.6 |
Financial services n.e.c. |
|
12.6.1 |
FISIM |
|
12.6.1.0 |
FISIM |
|
12.6.2 |
Other financial services n.e.c. |
|
12.6.2.1 |
Charges by banks and post offices |
|
12.6.2.2 |
Fees and service charges of brokers, investment counsellors |
|
12.7 |
Other services n.e.c. |
|
12.7.0 |
Other services n.e.c. |
|
12.7.0.1 |
Administrative fees |
|
12.7.0.2 |
Legal services and accountancy |
|
12.7.0.3 |
Funeral services |
|
12.7.0.4 |
Other fees and services |
ANNEX II
Correlation table
|
Regulation (EC) No 2494/95 |
This Regulation |
|
Article 1 |
Article 1 |
|
Article 2, point (a) |
Article 2, point (6) |
|
Article 2, point (b) |
— |
|
Article 2, point (c) |
— |
|
Article 3 |
Article 3(3) and (10) |
|
Article 4 |
Article 4(1), (2) and (4) |
|
Article 5(1)(b) |
Article 5(5) and (6) |
|
Article 5(3) |
Article 4(4) |
|
Article 6 |
Article 5(1) and (2) |
|
Article 7 |
Article 5(3) |
|
Article 8 |
Article 6(1), (3) and (4) |
|
Article 9 |
Article 3(1), (2) and (6) |
|
Article 10 |
Article 7(1) |
|
Article 11 |
— |
|
Article 12 |
Article 9(2) |
|
Article 13 |
— |
|
Article 14 |
Article 11 |
|
Article 15 |
— |
|
Article 16 |
Article 13 |
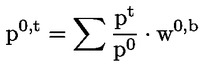
Leave a Reply